What Is A Fiber Forensics
Fiber analysis is a method of identifying and examining fibers used by law enforcement agencies around the world to procure show during an investigation. Fiber analysis is besides used by law enforcement agencies to place suspects at the scene of the crime. Transfer of fiber can occur during close contact with the victim or suspect. Fiber transfers can too occur during interruption-ins where fibers from the intruder are caught in.[1] [ii] Fiber evidence is a blazon of trace evidence, this means it volition likely be very small and sometimes could be microscopic.[3] This method is usually not used to actually pinpoint an offender in an investigation every bit information technology is not as reliable equally Dna.[1]
Fiber assay does not follow any officially laid-downwardly process. The most common use of fiber analysis is microscopic examination of both longitudinal and cantankerous sectional samples. While this is the most mutual method of undertaking fiber analysis, others practice exist. These include the burning and solubility methods. These methods are most commonly used to reveal the identity of the fiber. Fiber analysis is usually not undertaken in academy labs because of the usual lack of required solvents.[ii]
Methods [edit]
Scanning electron microscopy [edit]

SEM opened sample chamber
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is method of photography which requires an instrument called the scanning electron microscope, which uses electrons rather than light to form an image. In that location are many advantages to using the SEM instead of a light microscope. Using SEM requires a large depth of field, which allows a large corporeality of the sample to exist in focus at ane time.[four]
Diminutive strength microscopy [edit]

Atomic force microscopy is a method which is carried out using an atomic force microscope, which is an instrument that tin analyze and narrate samples at the microscopic level. The instrument allows the analyst to wait at surface characteristics with very accurate resolution ranging from 100 μm to less than i μm.[5]
Comparison Microscopy [edit]
Comparison microscopes are ofttimes used by analysts to wait at the general characteristics of the fibers. This technique is mostly but useful when comparing a known sample from a scene to a possible source. The analysts will look at a cantankerous section of the fibers under a comparing microscope and look at characteristics such as frays, cuts, striations, crimps, colour, thickness, and full general shapes inside the cobweb. The comparison microscope allows for 2 samples to be observed simultaneously. [3]
Dyes [edit]
There are many types of dyes and colours that are used on fibers. To help analysts narrow downwards their sample the American Association of Material Chemists generates a color index that contains all dyes and colours that are used on fibers. This allows analysts to compare their sample to known data in order to determine possible sources.[six]
Information technology is as well of import for analysts to know the types of dyes that can be used on fibers. The almost common list of dyes that are used tin be seen below.[3] These classes of dye are determined through how they are applied to fibers.[half dozen]
- Acid Dyes: used in basic weather condition, functional group of fiber is protonated and bonds to functional group of dye.[6]
- Basic Dyes: used in acidic atmospheric condition, functional group of fiber is deprotonated and bonds to functional grouping of dye.[half-dozen]
- Azoic Dyes: utilize diazo salt and a coupling amanuensis to dye fibers.[6]
- Direct Dyes: dye is practical using heat and electrolytes.[6]
- Disperse Dyes: Van der Waal forces and hydrogen bonding dye the fibers.[6]
- Metallized Dyes: metal complexes forms between the dye and fiber.[6]
- Sulfur Dyes: dye is reduced then oxidizes with the cobweb to bond, the dye becomes insoluble.[6]
- Vat Dyes: similar procedure to sulfur dyes, dye becomes insoluble with fiber once oxidation occurs.[half-dozen]
References [edit]
- ^ a b Ramsland, Katherine. "Trace Show". TruTV. Archived from the original on October iii, 2012. Retrieved April five, 2011.
- ^ a b A. Katz, David. "Study into Fiber assay" (PDF). Chymist.com. Retrieved April 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c Farah, Shady; Kunduru, Konda Reddy; Tsach, Tsadok; Bentolila, Alfonso; Domb, Abraham J. (April 30, 2015). "Forensic comparison of synthetic fibers". Polymers for Avant-garde Technologies. 26 (7): 785–796. doi:10.1002/pat.3540. ISSN 1042-7147.
- ^ "WHAT IS THE S.E.M.?". Iowa Country University. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved April 5, 2011.
- ^ "Atomic Force Microscopy: A Guide to Agreement and Using the AFM" (PDF). Texas State Academy. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 22, 2011. Retrieved April 6, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f thou h i j Goodpaster, John V.; Liszewski, Elisa A. (Baronial one, 2009). "Forensic analysis of dyed textile fibers". Belittling and Bioanalytical Chemical science. 394 (8): 2009–2018. doi:ten.1007/s00216-009-2885-7. ISSN 1618-2650.
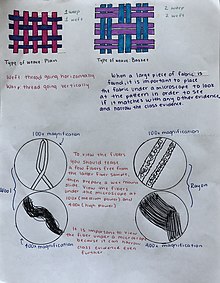
How fiber analysis works with large and pocket-size samples
What Is A Fiber Forensics,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fiber_analysis
Posted by: cravenalling69.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Fiber Forensics"
Post a Comment